Building RBDs from Lambda Predict
You can use the system configuration and failure rate predictions from Lambda Predict as a starting point for creating RBDs in BlockSim. As more information becomes available, you can then replace the predicted failure rate models with new models that are based on Weibull++ analyses and other sources.
Importing the system configuration data from Lambda Predict is a two-step process:
- First, you must publish the failure rates calculated
in Lambda Predict as reliability models. To do this, open
the project in Lambda Predict. In the prediction folio, select
the standard item (i.e.,
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  or
or  ) or assembly (i.e.,
) or assembly (i.e.,
 or
or  ) that you want
to create the RBD for, and then choose Prediction
Tools > Share > Publish Branch.
) that you want
to create the RBD for, and then choose Prediction
Tools > Share > Publish Branch.
![]()
Once the models are published, you can close the project in Lambda Predict if desired.
- Open the project in BlockSim, and then choose Home > Insert > Build RBDs and FTs from ReliaSoft Application.
![]()
When the window opens, specify that you want to use Lambda Predict as the data source in the ReliaSoft Application to Build From area. The utility will provide the following options:
- Simulation or Analytical - use the drop-down list to specify whether the new RBD(s) will be analytical diagrams or simulation diagrams.
- Create Folders - select this check box if you want the new diagram(s) to be organized into a separate folder in BlockSim's current project explorer. (Note that selecting this option can make it easier to delete and recreate the diagrams if you need to. You can delete the entire folder instead of deleting each diagram individually.)
- Create
subdiagrams for blocks - in this context, the term
"blocks" refers to the assemblies in Lambda
Predict. For each block in the prediction folio, you can:
- Use a single RBD block to represent the reliability of the entire assembly. This treats the assembly as a "black box" in the RBD, using the item model that was published for the block.
- Use a subdiagram in the RBD to represent the assembly. This allows you to consider the separate failure rates for all of the components that make up the assembly.
Note: For many of the reliability prediction standards available in Lambda Predict, a portion of the assembly's failure rate may be calculated at the block level. In Lambda Predict, this portion is called the block's supplemental model. For example, in MIL-217 analyses, the failure rate for a printed circuit board (PCB) assembly is a summation of the individual failure rates of its components plus the failure rate due to the physical connection of the components to the board. If you have chosen to create subdiagrams for such assemblies, the diagrams will contain the reliability models of all the components in the assembly plus the supplemental model that represents the failure rate due to the connections.
After you have specified your preferences, click Next to see the failure rate models that were published from Lambda Predict. As an example, the following pictures show two ways that models published from the same MIL-217 prediction might be displayed, depending on whether the Create subdiagrams for blocks option was selected.
In the first scenario, the Create
subdiagrams for blocks option was selected; therefore,
the utility displays all the assemblies ![]() and components
and components ![]() in the system configuration.
The window also displays the supplemental model
in the system configuration.
The window also displays the supplemental model ![]() for each assembly and
the item model
for each assembly and
the item model ![]() for each
component, as shown next. (Note that the supplemental model icon
will be displayed only if it's applicable for the particular assembly
and the model has been published from Lambda Predict.)
for each
component, as shown next. (Note that the supplemental model icon
will be displayed only if it's applicable for the particular assembly
and the model has been published from Lambda Predict.)
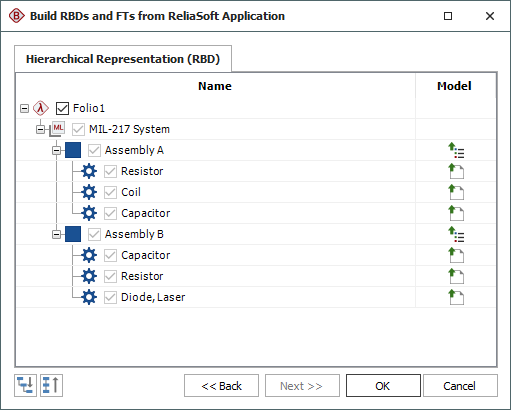
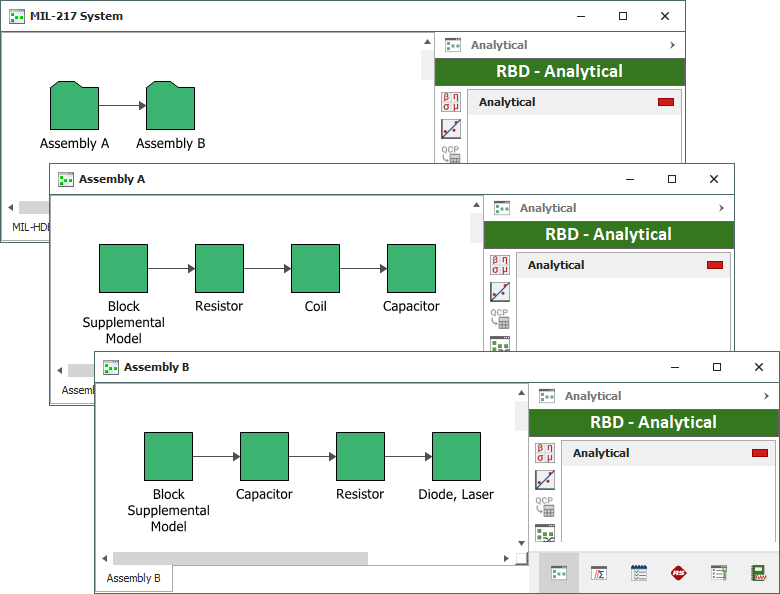
If you select all of the items shown in this hierarchy and click OK, BlockSim will create a diagram for the "MIL-217 System" that links to one subdiagram for Assembly A and another for Assembly B, as shown next.
In the second scenario, the Create
subdiagrams for blocks option was not selected; therefore,
the utility displays only the assemblies. In this case, the item
model ![]() that represents the failure rate calculated
for each assembly will be used.
that represents the failure rate calculated
for each assembly will be used.
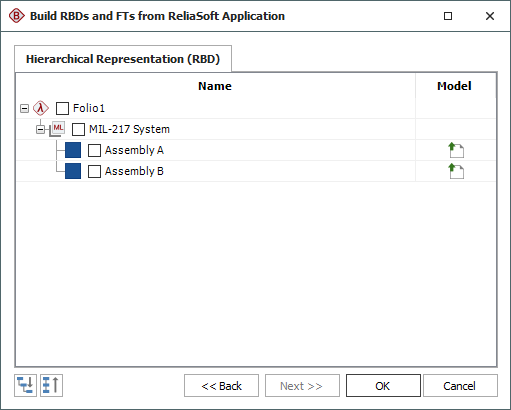
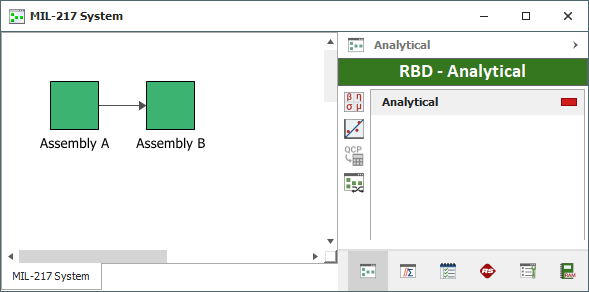
If you select all of the items shown in this hierarchy and click OK, BlockSim will create one diagram for the "MIL-217 System" that includes a single block for each assembly, as shown next.
Note the following:
- If you have made changes to the analysis in Lambda Predict since the last time you published the models, it is recommended to use the Publish Branch command to publish them again. If an item does not have a published model, it will not be included in the BlockSim diagram.
- Components with a value greater than 1 in their quantity field in Lambda Predict are represented by multi blocks.
- Parallel configurations at the assembly level, which Lambda Predict models using redundancy, are modeled in BlockSim using nodes.
- Component adjustment factors defined in Lambda Predict will be imported as block duty cycles. Adjustment factors for assemblies are not imported.
Any identifiers used in the Lambda Predict prediction are transferred as follows:
- For RBDs, folio identifiers are populated from the published model for the standard item or Lambda Predict block that the RBD represents.
- For subdiagram blocks, block identifiers are populated from the published model for the standard item or Lambda Predict block that the subdiagram represents.
- For blocks that represent components or, if the Create subdiagrams for blocks option is not selected, Lambda Predict blocks, both the block identifiers and the identifiers for the URD used by the block are populated from the published model for the component or Lambda Predict block.
- For blocks that represent supplemental block models, both the block identifiers and the identifiers for the URD used by the block are populated from the published model for the Lambda Predict block that the RBD represents.