Region and Language Settings
The Region and Language settings for your particular computer will have some impact on the way some information is displayed in ReliaSoft applications.
Users with different regional and language settings can work together on the same analysis projects because, in most cases, the basic information is stored in the database and the software simply displays it in the format preferred by each user. For example, if the date September 25, 2019 is stored in the database, User A might see it as "9/25/2019" while User B might see "25-Sep-19."
This topic first explains how to view or change the Region and Language settings on your computer and then discusses some specific considerations for ReliaSoft applications, including:
Viewing or Changing the Region and Language Settings for Your Computer
To view or change the region and language settings:
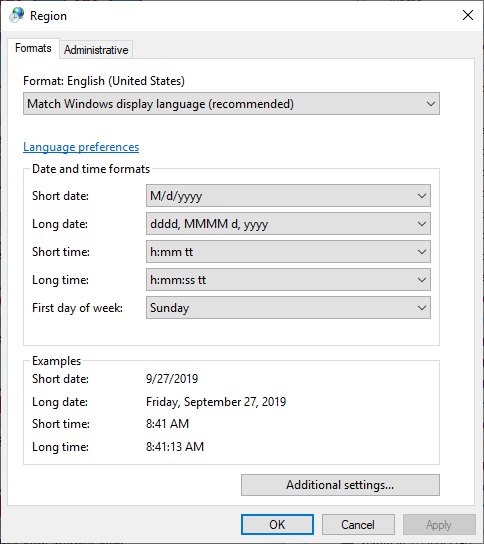
- In Windows 10, move the pointer to the lower left corner of the desktop, then right-click and choose Control Panel. Click the Clock and Region option then click the Region link.
As an example, the Windows 10 interface is shown here.
Other relevant settings are managed via the Customize Format window:
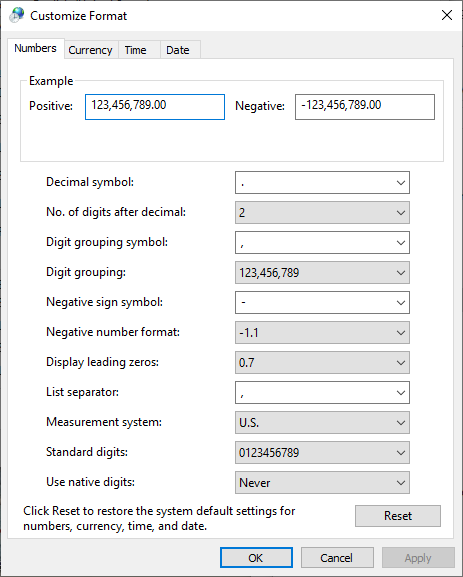
- In Windows 10, click the Additional settings button.
As an example, the Windows 10 interface is shown next.
Note: To see the changed settings in the ReliaSoft application, you must close the application, and then restart it.
Which Language is Selected by Default When You Install the Software
The user interface for ReliaSoft desktop applications is available in several languages. You can change this language at any time by choosing an option from the Language drop-down list on the Common Settings page of the Application Setup.
When you first install the software, it will check your computer's current language as it is set in the Format field in the Windows Region and Language window. If that language is supported in the ReliaSoft applications, they will use those settings; however, if that language is not supported, they will use the default setting of English.
Defining Date and Time Formats
Dates and times appear frequently throughout the ReliaSoft interface, including (but not limited to):
- The dates in the plot legend area of a plot in all ReliaSoft applications.
- The history provided throughout ReliaSoft applications (e.g., for resources, FMEA records, diagrams, in history logs, etc.).
- The dates in the worksheet view and in the record properties windows in XFMEA/RCM++ and MPC.
- The dates in the "dates of failure" format and "usage" format of the Weibull++ warranty folios.
The Short date field from the Windows Region and Language window determines how dates are displayed. You can select any standard format (e.g., M/d/yyyy, dd/MMM/yy, yy/MM/dd) or you can create your own format using the available date notations.
The Short time field determines how times are displayed. You can select any standard format (e.g., h:mm tt, HH:mm, HH'h'mm) or you can create your own format using the available time notations.
The Windows settings do not apply to the following items:
- Dates and times in spreadsheet utilities (e.g., a spreadsheet module in ReliaSoft Workbooks, General Spreadsheets, etc.).
- Dates and times displayed in the Weibull++ event log folio are created by the folio and are not affected by the computer's settings.
Changing the Decimal Symbol, the List Separator and the Currency Symbol
How decimal values are displayed depends on the value of the Decimal symbol field on the Numbers page of the Windows Customized Format window, which determines which character is used to indicate the decimal portion of a number (e.g., 85.25 or 85,25). In addition, the character used to separate the arguments in a list depends on the value of the List separator field. These settings affect how you enter functions in a spreadsheet module in ReliaSoft Workbooks or in General Spreadsheets, either manually or by using the Function Wizard.
For example, if the decimal symbol value is a comma, and the list separator value is a semicolon, you would enter a function like this: =RELIABILITY("Weibull!Folio1!Data 1";500;100;0,9)). Whereas, if the decimal symbol is a period and the list separator is a comma, it would be =RELIABILITY("Weibull!Folio1!Data 1",500,100,0.9)).
The currency symbol that is displayed in the software depends on the selection in the Currency symbol field on the Currency page of the Windows Customized Format window.