Design Folio Analysis Results
When accessed from a design folio, the Analysis
Summary window will contain detailed information about analysis
results, including information that describes how each factor
and factorial interaction affects the variation of the response
that is currently selected in the Data
tab control panel.
If the current response data has been analyzed, you can open
the window by clicking the View
Analysis Summary icon on the control panel.

If the current response data have not been analyzed, the icon
will still be available so you can view the folio's analysis history.
Analysis Results
Depending on the type of design you are working with, the analysis
results may contain some or all of the following:
The Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
table provides general information about the effects of
the factor(s) and factorial interactions on the selected response.
For designs with multiple factors, this information may be presented
for individual factors and interactions or for groups of factors
and interactions, depending on your analysis setting on the control panel.
 ANOVA
Table Columns
ANOVA
Table Columns
-
Source of Variation
is the source that caused the difference in the observed output
values. This can be a factor, factorial interaction, curvature,
block, error, etc. If your design includes more than one factor
and you have selected to use grouped terms in the analysis (specified
on the Analysis Settings page of the control panel), the effects
will be grouped by order (i.e., main effects, two-way interactions,
etc.). Sources displayed in red are considered to be significant.
-
The number of Degrees of
Freedom for the Model
is the number of regression coefficients for the effects included
in the analysis (e.g., two coefficients might be included in the
regression table for a given main effect). The number of degrees
of freedom for the Residual
is the total number of observations minus the number of parameters
being estimated.
-
Sum of Squares is
the amount of difference in observed output values caused by this
source of variation.
-
Mean Squares is
the average amount of difference caused by this source of variation.
This is equal to Sum of Squares/Degrees of Freedom.
-
F Ratio is the ratio
of Mean Squares of this source of variation and Mean Squares of
pure error. A large value in this column indicates that the difference
in the output caused by this source of variation is greater than
the difference caused by noise (i.e., this source affects the
output).
-
P Value (alpha error
or type I error) is the probability that an equal amount of variation
in the output would be observed in the case that this source does
not affect the output. This value is compared to the risk level
(alpha) that you specify on the Analysis Settings page of the
control panel. If the p
value is less than alpha, this source of variation is considered
to have a significant effect on the output. In this case, the
term and its p value
will be displayed in red.
-
The following values are shown underneath the ANOVA table,
and they indicate how well the model fits the data:
-
S is the standard
error of the noise. It represents the magnitude of the response
variation that is caused by noise. Lower values indicate better
fit.
-
R-sq is the
percentage of total difference that is attributable to the
factors under consideration. It is equal to Sum of Squares(factor)/Total
Sum of Squares. Higher values usually indicate better fit.
-
R-sq(adj) is
an R-sq value that is adjusted for the number of parameters
in the model. Higher values indicate better fit.
The Data
Summary table is available only for one factor designs.
It gives the mean and standard deviation of the output at each
level of the factor.
 Data
Summary Table Columns
Data
Summary Table Columns
- Factor Level
is the name of the qualitative level.
- Number in Level
is the number of data points obtained at the factor
level.
- Estimated Mean
is the average of the data points obtained at the
level.
- Standard Deviation is the standard deviation of the data points
obtained at the level.
The Mean
Comparisons table is available only for one factor
designs. It provides information on comparisons between factor
levels. The table includes the following columns:
 Mean
Comparisons Table Columns
Mean
Comparisons Table Columns
- Contrast
gives the paired comparison of any two levels. Level
1 - Level 2 means the difference between Level 1 and
Level 2. Contrasts displayed in red are considered
to be significant.
- Mean Difference
is the mean value of the difference in output between
the two levels.
- Pooled Standard
Error is the standard error of the mean difference
in output between the two levels.
- Low Confidence
is the lower confidence bound of the mean difference.
- High Confidence
is the upper confidence bound of the mean difference.
- T Value
is the normalized difference, which is equal to Mean
Difference/Pooled Standard Error.
- P Value
is the probability that an equal amount of variation
in the output would be observed in the case that there
is no significant difference between the levels. This
value is compared to the risk level (alpha) that you
specify on the Analysis Settings page of the control
panel. If the p
value is less than alpha, there is considered to be
a significant difference between the levels. In this
case, the contrast and its p
value will be displayed in red.
The Regression table
provides specific information on the contribution of each factor
or factorial interaction to the variation in the response and
an analysis of the significance of this contribution.
Note:
For each factor with n levels, n-1 effects are estimated (e.g.,
one effect is estimated for a two level factor, four effects are
estimated for a five level factor). For a two level factor, the
effect is the difference of the average response at the two levels.
For factors with more levels, the average response at one level
is considered to be a baseline and the average responses at other
levels are compared with that baseline. If more than one effect
exists for a factor, the effects are differentiated with a number
along with the factor’s letter designation (e.g., A[1], A[2]).
 Regression
Table Columns
Regression
Table Columns
-
Term is the factor,
factorial interaction, curvature, block, etc. under consideration.
Terms displayed in red are considered to be significant. In cases
where there is no error in the model, significant effects are
determined according to Lenth’s method and the term names are
displayed in red and followed by an asterisk (*).
-
Coefficient is the
regression coefficient of the term, which represents the contribution
of the term to the variation in the response.
-
Standard Error is
the standard deviation of the regression coefficient.
-
Low Confidence and
High Confidence
are the lower and upper confidence bounds on the regression coefficient.
-
T Value is the normalized
regression coefficient, which is equal to Coefficient/Standard
Error.
-
P Value (alpha error
or type I error) is the probability that an equal amount of variation
in the output would be observed in the case that this term does
not affect the output. This value is compared to the risk level
(alpha) that you specify on the Anaysis Settings page of the control
panel. If the p value
is less than alpha, this source of variation is considered to
have a significant effect on the output. In this case, the term
and its p value will
be displayed in red.
The Likelihood
table is available only for reliability designs. It provides
general information about the factor's effects on the times-to-failure.
 Likelihood
Table Columns
Likelihood
Table Columns
- Model
displays the model for which the results apply.
- Reduced
assumes that the product life is the same at different
levels of the factor.
- Full
assumes that the product life is different at
different levels of the factor.
- Degrees of
Freedom is the degrees of freedom of this source
of variation. This is also the number of parameters
in the model for this source.
- Ln(Likelihood
Value) is the logarithm transformation of the
likelihood value for this source of variation.
- Likelihood
Ratio is the likelihood ratio value for this
source of variation.
- P Value
is the probability that LR is from a chi-squared distribution,
which would indicate that the factor has no effect
on product life. This value is compared to the risk
level (alpha) that you specify on the Analysis Settings
page of the control panel. If the p
value is less than alpha, then the factor is considered
to have a significant effect on product life. In this
case, the effect and its p
value will be displayed in red.
The MLE Information table
is available only for reliability designs. It provides specific
information on the contribution of each factor or factorial interaction
to the variation in the times to failure and an analysis of the
significance of this contribution.
 MLE
Information Table Columns
MLE
Information Table Columns
- Term
is the factor, factorial interaction, etc. under consideration.
Terms displayed in red are considered to be significant.
- Effect
is a measure of how much the response value (Y) changes
when the value of the corresponding term in the model
(using coded values) changes from -1 to 1.
- Coefficient
is the regression coefficient of the term, which represents
the contribution of the term to the variation in the
response.
- Standard Error
is the standard deviation of the regression coefficient.
- Low Confidence
and High Confidence
are the confidence bounds on the regression coefficient,
using Fisher bounds.
- Z Value
is the normalized regression coefficient, which is
equal to Coefficient/Standard Error.
- P Value
is the probability that an equal amount of variation
in the output would be observed in the case that this
source does not affect the output. This value is compared
to the risk level (alpha) that you specify on the
Analysis Settings page of the control panel. If the
p value is
less than alpha, this source of variation is considered
to have a significant effect on the output. In this
case, the term and its p
value will be displayed in red.
The Life Characteristic Summary
table is available only for one factor reliability designs.
It gives the characteristic life and standard deviation for the
product at each factor level, along with lower and upper confidence
bounds.
 Life
Characteristic Summary Table Columns
Life
Characteristic Summary Table Columns
- Factor Level
is the name of the level.
- Number in Level gives the number of failures (F) and suspensions
(S) in the level.
- The next column is the characteristic life at
that level.
- Eta is shown for the Weibull distribution,
and it is equal to the time at which unreliability
= 63.2%.
- Ln-Mean is shown for the lognormal distribution,
and it is equal to the time at which unreliability
= 50%.
- MTTF (i.e., the mean time to failure) is shown
for the exponential distribution.
- The Standard
Deviation is also shown for the characteristic
life.
- Low Confidence
and High Confidence
give the two-sided confidence bounds on the characteristic
life, based on the risk level entered on the Analysis
Settings page of the control panel (e.g., if the risk
level is 0.1, then 90% two-sided bounds will be shown).
The Life Comparisons
table is available only for one factor reliability
designs. It provides information on comparisons between levels
of the factor, allowing you to determine whether one particular
level is significantly different from another.
 Life
Comparisons Table Columns
Life
Comparisons Table Columns
- Contrast
gives the paired comparison of any two levels. Level
1 - Level 2 means the difference between Level 1 and
Level 2. Contrasts displayed in red are considered
to be significant.
- Mean Difference
is the mean value of the difference in output between
the two levels.
- Pooled Standard
Error is the standard error of the mean difference
in output between the two levels.
- Low Confidence
is the lower confidence bound of the mean difference.
- High Confidence
is the upper confidence bound of the mean difference.
- T Value
is the normalized difference, which is equal to Mean
Difference/Pooled Standard Error.
- P Value
is the probability that an equal amount of variation
in the output would be observed in the case that there
is no significant difference between the levels. This
value is compared to the risk level (alpha) that you
specify on the Analysis Settings page of the control
panel. If the p
value is less than alpha, there is considered to be
a significant difference between the levels. In this
case, the contrast and its p
value will be displayed in red.
The Regression Equation information
is presented using multiple tables. The available tables will
vary depending on the design type you are working with. The results
that could be available include:
 Regression
Equation Tables
Regression
Equation Tables
-
The Response table
displays the response that the regression equation applies to
and the units of measurement that were entered for the response
(if any).
-
The Additional Settings
table shows the transformation and risk level you entered for
the response.
-
The Significant Terms table
is applicable only when at least one term was found to be significant.
It shows the significant terms in the Name column and the associated
regression coefficients in the Coefficient column.
-
The Equation tables
show the regression coefficients for the model of the selected
response. For example, consider this table:
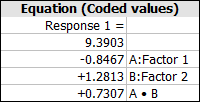
The corresponding model for this table is y = 9.3903 - 0.8467x1 + 1.2813x2
+ 0.7303x1x2.
Additional Results
All of the following tables provide information that was generated from
the main calculations. The available tables will vary depending on the
design type you are working with. The results that could be available
include:
 Alias
Structure
Alias
Structure
This item is available for all designs with
at least two factors. It describes the alias structure for the design,
taking into account only the terms
you've selected to include in the analysis. Together with your
engineering knowledge, you can use this information to help determine
whether any important interaction information was lost due to aliasing.
When aliased terms exist, the following areas will be shown:
-
-
Terms selected to be
in the model lists all the terms that are considered
for inclusion in the regression model (i.e., the selections
in the Select Terms window).
-
Terms included in the
model lists all the selected terms that are included
in the model. The alias structure determines which terms are
excluded.
-
Alias Structure
lists the aliased effects based on the selected terms. For
example, A • B = A • B + C • D means the interaction effect
A • B is aliased because it is indistinguishable from effect
C • D. Therefore, the model cannot include both interaction
terms; it will include only one (e.g., A • B).
 Alias
Summary
Alias
Summary
The terms in the first column of this table
are aliased with the terms shown in the second column. Only the terms
in the first column are included in the model.
 Var/Cov
Matrix
Var/Cov
Matrix
This shows the variance/covariance matrix,
which is available for one factor R-DOE designs and all other designs
with two or more factors. The diagonal elements in this matrix are
used to calculate the coefficients in the MLE or Regression Information
table.
 Diagnostic
Information
Diagnostic
Information
This table is available
for one factor R-DOE designs and all other designs with two or more
factors. It displays various analysis results for each run and highlights
significant values. The following columns are included:
-
-
Run Order
is the randomized order, generated by the software, in which
it is recommended to perform the runs to avoid biased results.
Note that any changes made to the Run Order column on the
Data tab will be reflected here.
-
Standard
Order is the basic order of runs, as specified in the
design type, without randomization. Note that any changes
made to the Standard Order column on the Data tab will be
reflected here.
-
Actual
Value (Y) is the observed response value for the run,
as entered in the response column on the Data tab.
-
Predicted
Value (YF) is the response value predicted by the model
given the factor settings used in the run.
-
Residual
(or "regular residual") is the difference between
the actual value (Y) and the predicted value (YF) for the
run.
-
Standardized
Residual is the regular residual for the run divided
by the constant standard deviation across all runs.
-
Studentized
Residual is the regular residual for the run divided
by an estimate of its standard deviation.
-
External
Studentized Residual is the regular residual for the
run divided by an estimate of its standard deviation, where
the run in question is omitted from the estimation.
-
Leverage
is a measure of how much the run influences the predicted
values of the model, stated as a value between 0 and 1, where
1 indicates that the actual response value of the run is exactly
equal to the predicted value (i.e.
the predicted value is completely dependent upon the observed
value).
-
Cook’s
Distance is a measure of how much the output is predicted
to change if the run is deleted from the analysis.
Values that are considered to be significant,
or outliers, are displayed in red. For the residual columns, significant
or critical values are those that fall outside the residual’s upper
or lower bounds, calculated based on the specified alpha (risk) value.
The ReliaWiki resource portal has more information
on how significant values are determined for the Leverage and Cook's
Distance columns at: http://www.reliawiki.org/index.php/Multiple_Linear_Regression_Analysis.
 Least
Squares Means
Least
Squares Means
This table shows the predicted response values
for the given factor levels. It includes the following columns:
-
-
Effect is the
main effect or interaction used to predict the response. The
coefficients for effects not used in the prediction are set
to zero.
-
Level is the
combination of factor levels used to predict the response.
-
Mean is the
predicted response value.
 Regressor
Regressor
This table is available only for mixture
designs. It shows the values of each term used in the regression
equation (whereas the Regression Equation table shows the
coefficients).
![]()
![]() Mean
Comparisons Table Columns
Mean
Comparisons Table Columns
![]() Life
Characteristic Summary Table Columns
Life
Characteristic Summary Table Columns
![]() Life
Comparisons Table Columns
Life
Comparisons Table Columns
