VAR
Used only in ReliaSoft Workbooks
Description: Estimates variance based on a sample (ignores logical values and text in the sample).
Syntax: VAR(Number1, Number2, ...)
- Number1, Number2, ... are 1 to 30 number arguments corresponding to a sample of a population.
Remarks:
- VAR assumes that its arguments are a sample of the population. If your data represents the entire population, then compute the variance by using VARP.
- Arguments can either be numbers or names, arrays or references that contain numbers.
- Logical values, and text representations of numbers that you type directly into the list of arguments are counted.
- If an argument is an array or reference, only numbers in that array or reference are counted. Empty cells, logical values, text or error values in the array or reference are ignored.
- Arguments that are error values or text that cannot be translated into numbers cause errors.
- VAR uses the following formula:
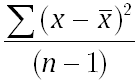
where x is the sample mean AVERAGE(Number1, Number2,…) and n is the sample size.
Example:
Suppose 10 tools stamped from the same machine during a production run are collected as a random sample and measured for breaking strength. The sample values (1345, 1301, 1368, 1322, 1310, 1370, 1318, 1350, 1303, 1299) are stored in A2:A11, respectively. VAR estimates the variance for the breaking strength of the tools.
- VAR(A2:A11) = 754.2666667 [the variance for the breaking strength of the tools]